Learn the basics of capacitors
Learn the basics of capacitors
Learn the basics of capacitors
Views: 0 - Post on: 29/09/2022
What is a capacitor?
Capacitor – English name is called Capacitor, denoted by C in the circuit. This is a kind of passive electronic component. They are made up of two conductive surfaces separated by a dielectric. When there is a difference in potential at the two surfaces. There will be charges of the same amount but opposite signs.
This is a component that is considered to be quite important among the 5 components of electronic equipment. And is an indispensable component in filter circuits, oscillator circuits and AC signal transmission circuits.
Construction of the capacitor
Basically, their structure consists of two metal poles placed in parallel. And has DC insulation properties. But for alternating current to pass through the charge-discharge principle.
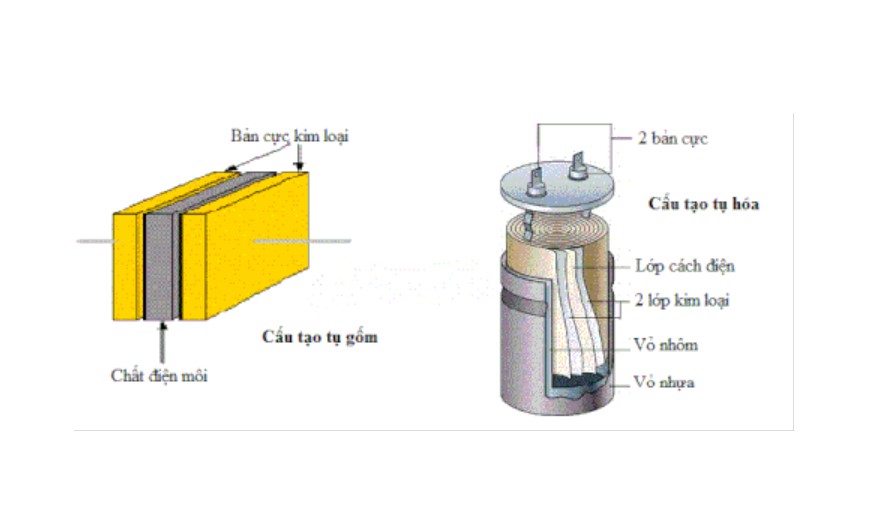
Between the two plates there is a medium known as the dielectric or non-conductive medium. Here the dielectric can be made from paper, air, ceramic, glass or rubber, etc. Usually people will depend on the dielectric construction material to name the corresponding capacitor.
Working principle
In an electrical circuit, capacitor C will usually be connected to two or more electrical conductors (which can be in the form of a metal plate or a surface separated by a dielectric medium).
In it, an electrical conductor can be in the form of a foil or a thin film or an electrolyte. Because the dielectric in the capacitor is not capable of conducting electricity. So it will increase the capacity to charge. When a capacitor is mounted on a battery, the dielectric creates an electric field with a positive and negative charge that builds up on the surface.
Characteristics
Capacitors’ ability to store energy in the form of electric field energy is formed by the accumulation of charges on two surfaces.
When the two surfaces are alternating current, a potential difference occurs. Charge accumulation is behind in phase with respect to voltage. And make up the impedance of the capacitor in the AC circuit.
In a normal C capacitor, they are capable of discharging from the anode to the cathode.
The main parameters of the capacitor
Capacitance of the capacitor
Capacitance of a capacitor is used to evaluate an object’s ability to hold a charge. In a capacitor, the capacitance C will be dependent on the plate charge. The dielectric material and the distance between the plates. The larger the capacitance, the longer the charge time of the capacitor and vice versa.
Fara (F). However, there are some cases where 1 Fara has a very large value and in practice people often use smaller units such as: pico fara, nano fara, micro fara
Voltage
In capacitor C the highest voltage in the working capacity will be written on the capacitor body, characterizing its withstand capacity.

The instantaneous voltage value may be higher than the capacitor working voltage value. But if there is a case where the value is too high, the dielectric layer can be broken and cause a short circuit.
In real life, when choosing a capacitor for a circuit, it is necessary to choose a capacitor with a working voltage that is about 30% higher than the upper circuit voltage.
Working temperature
This is the temperature in the area where the capacitor is located when the circuit is operating. It is necessary to select the highest operating temperature of the capacitors and must be higher than the temperature in the area where they are located.
Heat will be generated as the electrical energy of the circuit is converted to heat and the heat converted to heat in the capacitors causes the temperature inside them to be higher than the surrounding, causing some damage or possibly explosion.
Classify:
There are many different types of capacitors on the market today, but basically, they will be divided into 2 main types. Includes: polarized capacitors with defined polarities and non-polarized types because no specific polarity is specified. We can refer to some more commonly used types of capacitors today:
Convergence of:

Capacitors are typical polarized C capacitors. When using the type they need to pay attention to plug the correct pins of the capacitor with the corresponding voltage. On their bodies, there will usually be instructions for users with + or – symbols corresponding to the capacitor pins.
Capacitors have two common types of capacitors: capacitors with 2 pins on the same end and capacitors with 2 different pins on their heads.
On the capacitor will also often be listed with the maximum voltage value that it can withstand. In some cases where the voltage level is higher than the voltage on the capacitor, it may swell or may explode.
The value of the capacitor is usually written directly on the body. Depending on the different values, the capacitor will be applied in circuits with different frequencies or used to filter the source for normal capacitors.
In fact, people will often use electrolytic capacitors with a voltage value greater than the voltage passed through to ensure good operation and ensure their life.
Non-polar capacitors: ceramic capacitors, paper capacitors, mica capacitors

These will usually be small flat capacitors and do not distinguish positive and negative poles. They usually have a fairly small capacitance below 0.47 µF.
The value of this type will usually be marked on the capacitor body. For example: 103J, 223k. In which the first 3 numbers represent the value, the last letter will represent the error.
This non-polarized type usually withstands high voltages of 50V or 250V. Therefore, they are commonly used in high frequency circuits or noise filtering circuits.
Rotating Capacitor- Variable Capacitor

This type of capacitor usually has a very small value, usually ranging from 100 µF – 500 pF. They can rotate by themselves to change the capacitance value. Preferably used in radio tuning circuits. To change the resonant frequency when tuning.
Super Capacitor
Supercapacitors are capacitors with extremely high energy density. They are polarized and are used for DC charging. They can store electricity for several months or provide power instead of data storage batteries in electronic machines.
Practical application.
Capacitors have the ability to store electricity like a battery, plus the ability to charge and discharge electricity very quickly. That’s why it doesn’t waste energy. Moreover, it is also quite small in size, much more convenient during use.
Because of their fairly rapid discharge, they can also conduct AC.
They help to reduce the ripple of the power source steadily in AC power sources. For alternating current should choose short circuit type. As for the DC current, it is advisable to choose the open circuit type.
Capacitor C is commonly and quite widely used in engineering and electronics. In today’s electronic devices, they are quite commonly used. And has an important role in the operation of the circuit.
With main function for AC voltage to pass through. As well as the ability to prevent DC voltage. Helps the signal transmission stage between the amplifier stages with the difference in DC voltage.
On the principle of operation of source filter capacitors, they can filter AC voltage. After that is main saved into a flat DC voltage.
It has the function of conducting electricity with AC voltage and filtering for DC voltage.







